Butt-weld Fittings allow for changing the direction of flow, reducing pipe sizes and attaching auxiliary equipment..
Manufacturing standards are governed under ANSI/ASME B 16.9. Butt-Weld Fittings are available in variety of kinds such as tees, caps, elbows, reducers and outlets.
![201903301019011964.png ((QMO$GNQQ8MSDAJEH1SE]J.png](https://zjchuhaioss.oss-us-west-1.aliyuncs.com/201903301019011964.png)
Welded pipe fittings in carbon steel and stainless steel are the joining components that make possible the assembly of valves, pipes and equipment onto the piping system. Welded fittings compliment pipe flanges in any piping system and allows;
Change direction of flow in a piping system
Connect or joint pipes and equipment
Provide branches, access and takeoffs for auxiliary equipment
A common example using welded pipe fitting is a pipe reduced by concentric reducer, welded to a weld neck flange and connected to an equipment. Figure below represent complete collection of butt welded pipe fitting
The benefit to using a butt weld fitting is that it doesn’t leak. Because the butt weld is welded directly to pipe and not simply bolted together, it is not only much stronger than a typical fitting, but it allows for better flow through the system with less resistance to friction. Welded fittings also allows for better layout designs through key features such as being more compact and greater in strength.
Welded connection offers a more robust connection
Continuous metal structure adds to the strength of the piping system
Buttweld fittings with matching pipe schedules, offers seamless flow inside the pipe. A full penetration weld and properly fitted LR 90 Elbow, Reducer, Concentric reducer etc. offers gradual transition via welded pipe fitting.
Option of various turn radius using Short Radius (SR), Long Radius (LR) or 3R Elbows
Cost effective compared to their expensive threaded or socket weld counter parts.
Stainless Steel Welded Fittings are also available in SCH 10, allowing a more thinner wall option.
Stainless Steel Butt Weld Fittings are more common in SCH 10 and SCH 40 configuration.
All butt weld fittings have beveled ends as per ASME B16.25 standard. This helps create full penetration weld without any extra preparation needed for the butt weld fitting.
Butt weld pipe fittings are most commonly available in carbon steel, stainless steel, nickel alloy, aluminum and high yield material. High yield butt weld carbon steel pipe fittings are available in A234-WPB, A234-WPC, A420-WPL6, Y-52, Y-60, Y-65, Y-70. All WPL6 pipe fittings are annealed and are NACE MR0157 and NACE MR0103 compatible.
Materials & Specifications
Standard Grades: Carbon, Stainless, Chrome Moly, High Yield, Low Temperature, Aluminum
Types: Elbows, Tees, Reducers, Caps, Stub Ends, Crosses, Laterals, Olets, Return Bends
Sizes: Standard 1/2" to 48" (special order larger O.D. fittings)
Wall Sizes: Schedule 20 thru XXH, and Special Wall Sizes
Specialty Items: 3D & 5D Bends, Galvanizing, 100% X-ray Testing
Carbon Steel | WPB, WPC, WPL6 |
Chrome Moly | WP5, WP9, WP11, WP12, WP22 |
Stainless Steel | 304/304L, 316/316L, 304H, 316H, 309, 310S, 317L, 321/321H, 347/347H, 904L, DUPLEX 2205 / SUPER DUPLEX 2507 |
High Yield Carbon Steel | WPHY42, WPHY52, WPHY65 |
Nickel Alloys | Alloy 20, 200, 201, 400, 600, 625, 800H/HT, 825, 254SMO, AL6XN, C276, C22, B3, HAST-X |
Forged Steel buttweld fittings are manufactured in accordance with ANSI / ASME B16.9.
We will help you put together your entire project and ship it to your closest port.
These fittings are the most common type of welded pipe fitting and are specified by nominal pipe size and pipe schedule. Buttweld fittings use seamless or welded pipe as the starting material and are forged (through multiple process) to get he shape of elbows, tees and reducers etc.
ASME B16.25 sets standards for the preparation of the ends of components that need to be welded together.

Cut square or slight chamfer, at manufacturer’s option for :
t ≤ 0.19” carbon steel or ferritic alloy steels
t ≤ 0.12” austenitic alloy steels
 The allowable pressure ratings for fittings designed in accordance with the standard ASME B 16.9–1993 may be calculated as for straight seamless pipe in accordance with the rules established in the applicable section of the ASME B 31 codes for pressure piping.
The allowable pressure ratings for fittings designed in accordance with the standard ASME B 16.9–1993 may be calculated as for straight seamless pipe in accordance with the rules established in the applicable section of the ASME B 31 codes for pressure piping.
are strong and leak-proof
minimize the pressure drops and the turbolence along the pipeline
have a long service life
There are four different type of connections that are used for fittings:
Butt Weld Fittings – Probably the most common type of fitting. They are easily manufactured and are easily installed. Butt weld fittings can be connected directly to each other. This is called fitting make up.
Flanged Fittings – Flanged fittings are piping components where the flange is an integral component of the fitting. These are most often used in water treatment applications or lined piping where welding would be destructive to the liner.
Socket Weld Fittings – These fittings have a socket weld connection on each end. They might be used for smaller diameter piping. These fittings utilize a single fillet weld to join the piping with the fitting.
Threaded Fittings – Threaded fittings are generally four inches and smaller. The reason for this size constraint is the pipe end needs to be threaded with a male type connection and die sizes are unobtainable in the larger diameters.
ASME buttweld fitting specifications do not specify weights for fittings.
Weights quoted in the tables on this page are based on manufacturers information and should be considered as approximate and provided as a guide only (fitting weights can vary considerably between manufacturers due to differences in construction).
A pipe fitting is defined as a part used in a piping system, for changing direction, branching or for change of pipe diameter, and which is mechanically joined to the system.
There are many different types of fittings and they are the same in all sizes and schedules as the pipe.
Fittings are divided into three groups:
Buttweld (BW) fittings whose dimensions, dimensional tolerances et cetera are defined in the ASME B16.9 standards. Light-weight corrosion resistant fittings are made to MSS SP43.
Socket Weld (SW) fittings Class 3000, 6000, 9000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
Threaded (THD), screwed fittings Class 2000, 3000, 6000 are defined in the ASME B16.11 standards.
Fittings are used wherever liquids, gases, chemicals and other fluids are created, processed, transported, or used.
Energy related.
Oil and gas industries, including upstream (exploration and production), midstream (transportation by ships, pipeline, rail, trucks; storage and wholesale) and downstream (refining into fuels or chemicals; marketing and distribution). Power plants using fossil or nuclear fuels. Geothermal energy for harnessing heat from the earth.
Food and beverage production.
From basic ingredients to elaborate desserts. From milk, to juices and other beverages. Cold chain to keep produce fresh, drinks and frozen foods at a set temperature. Desalination plants to transform seawater into drinking water for arid areas and various tropical islands.
Pharmaceuticals and biotech production.
Medicines and vaccines that treat illnesses and help restore bodies and minds to their top conditions.
Semiconductor manufacturing:
Microchips that go into all electronics, including smartphones, tablets, computers, television sets, telecom networks …
Pulp and paper production.
Newsprint, glossy paper, cardboard boxes, books, writing paper
Production of construction materials and plastics. From roofing materials, to glassmaking for windows, to copper wiring for transporting electricity, and various plastics throughout houses and office buildings.

Fittings may be made to special dimensions, sizes,shapes, and tolerances by agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
Welding Bevel acc. to
ASME B16.9, Factory-Made Wrought Steel Buttwelding Fittings
ASME B16.28, Buttwelding Short Radius Elbows and Returns
ANSI/ASME B16.25, Buttwelding Ends
MSS SP-97, Socket Welding, Threaded, and Buttwelding Ends
The endr 5 mm for ferritic stainless steel. The shape of the bevel depending upon the actual wall thickness. This bevelled ends are needed to be able to make a "Butt weld".
Welding Bevel acc.to ASME / ANSI B16.9 and ASME / ANSI B16.28
ASME B16.25 covers the preparation of buttwelding ends of piping components to be joined into a piping system by welding. It includes requirements for welding bevels, for external and internal shaping of heavy-wall components, and for preparation of internal ends (including dimensions and dimensional tolerances).
Our in-hourse R&D team developed bevel ends equipment are good using in thickness 2mm to 20mm pipe fittings, guarantee high efficiency and high quality.
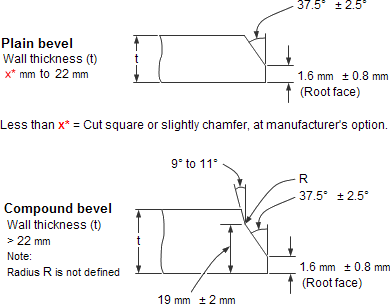
These weld edge preparation requirements are also incorporated into the ASME standards (e.g., B16.9, B16.5, B16.34).









Tel:
E-mai:
Skype: